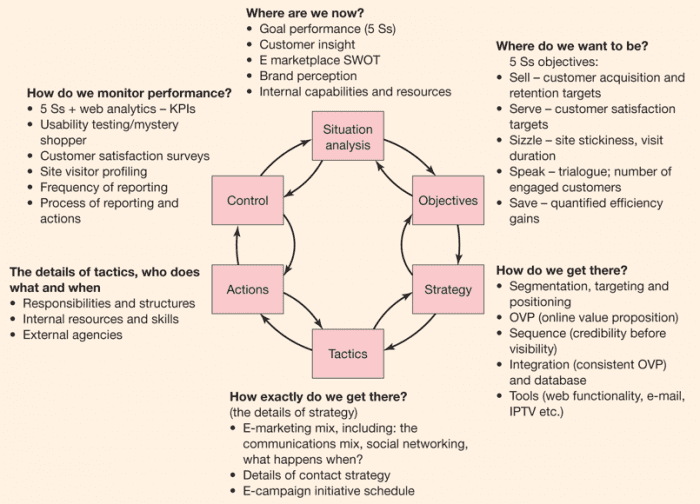
This article is about the idiom referring to excessive bureaucratic regulation. For other uses, see Red tape (disambiguation).
Red tape is an idiom referring to regulations or conformity to formal rules or standards which are claimed to be excessive, rigid or redundant, or to bureaucracy claimed to hinder or prevent action or decision-making. It is usually applied to governments, corporations, and other large organizations. Things often described as “red tape” include filling out paperwork, obtaining licenses, having multiple people or committees approve a decision and various low-level rules that make conducting one”s affairs slower, more difficult, or both.[1][2][3] Red tape has been found to hamper organizational performance and employee wellbeing by a recent meta-analysis of research studies.[4]
Contents
1 Origins 2 Red tape reduction 3 See also 4 References 5 Further reading
Origins
Bundle of US pension documents from 1906 bound in red tape
It is generally believed that the term originated with the Spanish administration of Charles V, King of Spain and Holy Roman Emperor, in the early 16th century, who started to use red tape in an effort to modernize the administration that was running his vast empire. The red tape was used to bind the most important administrative dossiers that required immediate discussion by the Council of State, and separate them from issues that were treated in an ordinary administrative way, which were bound with ordinary string.[5]
Although they were not governing such a vast territory as Charles V, this practice of using red tape to separate the important dossiers that had to be discussed was quickly copied by the other modern European monarchs to speed up their administrative machines.
In this age of civil servants using computers and information technology, a legacy from the administration of the Spanish Empire can still be observed where some parts of the higher levels of the Spanish administration continue the tradition of using red tape to bind important dossiers that need to be discussed and to keep them bound in red tape when the dossier is closed. This is, for example, the case for the Spanish Council of State, the supreme consultative council of the Spanish Government. In contrast, the lower Spanish courts use ordinary twine to bundle documents as their cases are not supposed to be heard at higher levels.[citation needed ] The Spanish Government plans[when? ]to phase out the use of paper and abandon the practice of using twine.[citation needed ]
The tradition continued through to the 17th and 18th century. In David Copperfield, Charles Dickens wrote, “Britannia, that unfortunate female, is always before me, like a trussed fowl: skewered through and through with office-pens, and bound hand and foot with red tape.” The English practice of binding documents and official papers with red tape was popularized in Thomas Carlyle”s[6] writings, protesting against official inertia with expressions like “Little other than a red tape Talking-machine, and unhappy Bag of Parliamentary Eloquence”. To this day, most defense barristers” briefs, and those from private clients, are tied in a pink-coloured ribbon known as “pink tape” or “legal tape”.
Even in modern times, Spanish bureaucracy is notorious for unusually extreme levels of red tape (in the figurative sense).[7] As of 2013, the World Bank ranked Spain 136 out of 185 countries for ease of starting a business, which took on average 10 procedures and 28 days.[8] Similar issues persist throughout Latin America.[7][9] As of 2009 in Mexico, it took six months and a dozen visits to government agencies to obtain a permit to paint a house,[10] and to obtain a monthly prescription for gamma globulin for X-linked agammaglobulinemia a patient had to obtain signatures from two government doctors and stamps from four separate bureaucrats before presenting the prescription to a dispensary.[11]
Red tape reduction
The expression “cutting of red tape” generally refers to a reduction of bureaucratic obstacles to action. It is also used as a cover to justify the reduction or removal of protective standards or regulations.
Business representatives often claim red tape is a barrier to business, particularly small business. In Canada, the Canadian Federation of Independent Business[12] has done extensive research[13] into the impact of red tape on small businesses.
The European Commission has a competition that offers an award for the “Best Idea for Red Tape Reduction”. The competition is “aimed at identifying innovative suggestions for reducing unnecessary bureaucracy stemming from European law”.[14] In 2008, the European Commission held a conference entitled “Cutting Red Tape for Europe”. The goal of the conference was “reducing red tape and overbearing bureaucracy,” in order to help “business people and entrepreneurs improve competitiveness”.[15]
See also
Busy work Instruction creep Micromanagement Paperwork Reduction Act Paternalism Prig Purple crocodile Sir Humphrey Appleby
References
^ “red tape: Definition from”. Answers.com. Retrieved 2012-10-09 . ^ “What is red tape? definition and meaning”. Businessdictionary.com. Retrieved 2012-10-09 . ^ “Red Tape Reduction Initiative | Business”. Gov.nl.ca. Archived from the original on 2012-11-09. Retrieved 2012-10-09 . ^ George, Bert; Pandey, Sanjay K.; Steijn, Bram; Decramer, Adelien; Audenaert, Mieke (2020). “Red tape, organizational performance and employee outcomes: meta-analysis, meta-regression and research agenda”. Public Administration Review. n/a (n/a). doi:10.1111/puar.13327. hdl:1854/LU-8683417 . ISSN 1540-6210. ^ Dickson, Del (2015). The People”s Government: An Introduction to Democracy. New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 176. ISBN 9781107043879. Retrieved 13 December 2015 . ^ p.1152, Brewer”s Dictionary of Phrase & Fable, 17th Edition; Revised by J Ayto, 2005 ^ a b Graff, Marie Louise (2009). CultureShock! Spain (6th ed.). Tarrytown, NY: Marshall Cavendish. p. 57. ISBN 9789814435949.
Bạn đang xem: Red tape là gì
Xem thêm: Trẻ Trâu Là Gì – Tính Trẻ Trâu Là Tốt Hay Xấu
Xem thêm: Thermocouple Là Gì – Cảm Biến Nhiệt độ
^ Buck, Tobias (2 June 2013). “Spain hopes new law to cut red tape will attract entrepreneurs”. Financial Times. The Financial Times Ltd. Retrieved 13 December 2015 . ^ Jose Luis Guasch; Benjamin Herzberg (2008). “Increasing Competitiveness Through Regulatory and Investment Climate Improvements in Latin America; the Case of Mexico”. In Haar, Jerry; Price, John (eds.). Can Latin America Compete? Confronting the Challenges of Globalization. New York: Palgrave Macmillan. p. 255. ISBN 9781403975430. ^ Ellingwood, Ken (2 January 2009). “No stamp of approval for Mexico bureaucrats”. Los Angeles Times. Tribune Publishing Company. Retrieved 13 December 2015 . ^ Malkin, Elizabeth (8 January 2009). “For Redress of Grievances, Mexicans Turn to Bureaucracy Contest”. New York Times. New York Times Company. Retrieved 13 December 2015 . ^ “cfib.ca”. cfib.ca. Retrieved 2014-01-23 . ^ “Canada”s Red Tape Report”. Cfib-fcei.ca. Archived from the original on 2014-02-01. Retrieved 2014-01-23 . ^ European Commission[dead link ] ^ Verheugen, Günter (June 20, 2008). “Cutting redTape for Europe”. Action Programme for Reducing Administrative Burdens in the European Union. European Commission Directorate-General Enterprise and Industry. Archived from the original on July 20, 2011. Retrieved October 14, 2020 .
Further reading
George et al. (2020) Red Tape, Organizational Performance and Employee Outcomes: Meta-Analysis, Meta-Regression and Research Agenda. Public Administration Review. Barry Bozeman (2000) Bureaucracy and Red Tape Prentice-Hall Publishing. Pamela Herd (2019). Administrative Burden: Policymaking by Other Means. Russell Sage Foundation. ISBN 978-0871544445. OECD (2006) “Cutting red tape; national strategies for administrative simplification” OECD Editions, Paris.
Chuyên mục: Hỏi Đáp