Bạn đang xem: Hộ tịch tiếng anh là gì
2. The competence and procedures for settling matters related tocitizenship and adoption must comply with the Law on Vietnamese Citizenship andthe Law on Adoption, unless otherwise provided by this Law.
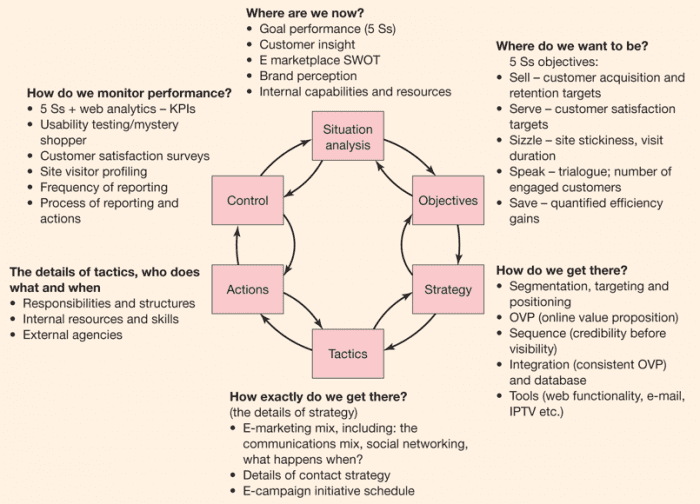
1. Civil status means events prescribed in Article 3 of this Law, whichdetermine the personal history of an individual from birth to death.
2. Civil status registration means a competent state agency certifyingor recording in the civil status book civil status events of an individual,creating a legal basis for the State to protect lawful rights and interests ofthe individual and manage the population.
dd/ Civil status change and correction; ethnicity re-determination,civil status information addition;
2. Recording in the civil status book civil status changes of anindividual according to a judgment or decision of a competent state agency:
g/ Declaration or cancellation of declaration of a person to be missing,dead or have civil act capacity lost or restricted.
3. Recording in the civil status book the events of birth; marriage;divorce; marriage cancellation; guardianship; parent or child recognition; parentor child determination; adoption; civil status change; and death of Vietnamesecitizens already settled at competent foreign agencies.
4. Certifying or recording in the civil status book other civil statusmatters in accordance with law.
1. Civil status registration agency is the People’s Committee of acommune, ward or township (below referred to as commune-level People’sCommittee), the People’s Committee of a rural district, urban district, town orprovincial city or an equivalent administrative unit (below referred to asdistrict-level People’s Committee) or an overseas Vietnamese diplomatic missionor consular office (below referred to as representative mission).
2. Civil status database means a collection of civil status informationof individuals already registered and stored in the civil status book andelectronic civil status database.
3. Civil status book means a paper book made and kept at the civilstatus registration agency to certify or record civil status events specifiedin Article 3 of this Law.
4. Electronic civil status database means a sectoral database created onthe basis of computerization of civil status registration work.
5. Civil status database-managing agency means the civil statusregistration agency, the Ministry of Justice, the Ministry of Foreign Affairsor another agency as assigned in accordance with law.
6. Birth certificate means a document granted by a competent stateagency to an individual upon birth registration; a birth certificate containsbasic personal information specified in Clause 1, Article 14 of this Law.
7. Marriage certificate means a document issued by a competent stateagency to the male and female partners upon marriage registration; a marriagecertificate contains basic information specified in Clause 2, Article 17 ofthis Law.
8. Native place of an individual shall be determined based on the nativeplace of his/her father or mother as agreed upon by the father and mother oraccording to practices and written in the birth declaration form submitted uponbirth registration.
9. Civil status extract means a document issued by a competent stateagency proving a civil status event of an individual already registered at acivil status registration agency. The original civil status extract shall beissued immediately after a civil status event is registered. Copies of a civilstatus extract include copies of civil status extracts issued from the civilstatus database and certified copies of original civil status extracts.
10. Civil status change means a competent state agency registeringchanges in civil status information of an individual when there is a plausiblereason in accordance with the civil law or changes in information about parentsin the registered birth declaration contents in accordance with law.
11. Ethnicity re-determination means a competent state agencyregistering the ethnicity re-determination for an individual in accordance withthe Civil Code.
12. Civil status correction means a competent state agency correctingcivil status information of an individual when there is an error in the civilstatus registration.
13. Civil status supplementation means a competent state agency updatingmissing civil status information for a registered individual.
2. All civil status events of an individual shall be registered in afull, prompt, truthful, objective and accurate manner; for cases ineligible forcivil status registration as prescribed by law, heads of civil statusregistration agencies shall issue written refusal replies clearly stating thereason.
3. Civil status matters for which no settlement time limit is prescribedby this Law shall be settled within the day; for dossiers received after 15:00hours which cannot be settled immediately, results shall be given in thefollowing working day.
4. Every civil status event shall be registered at only one competentcivil status registration agency in accordance with this Law.
An individual may make civil status registration at the civil statusregistration agency in his/her registered place of permanent or temporaryresidence or the place where he/she is living. For an individual who does notregister in his/her place of permanent residence, the district-level People’sCommittee, commune-level People’s Committee or representative mission which hasregistered such individual’s civil status shall notify the civil statusregistration to the commune-level People’s Committee of the place where he/shepermanently resides.
5. Once having been registered in the civil status book, every civilstatus event shall be fully and promptly updated in the electronic civil statusdatabase.
Xem thêm: Expenditure Là Gì – Tìm Hiểu Expenditure Trong Kế Toán
6. Contents of birth, marriage, divorce, death, civil status change,correction or supplementation, gender re-assignment and ethnicityre-determination of an individual in the civil status database are inputinformation of the national population database.
1. Vietnamese citizens and stateless persons permanently residing in Vietnamhave the civil status registration right and obligation.
This provision also applies to foreign citizens permanently residing inVietnam, unless otherwise provided by a treaty to which Vietnam is acontracting party.
2. In case of marriage or parent or child recognition, the parties shalldirectly register it at the civil status registration agency.
For other matters of civil status registration or issue of civil statusextract copies, requesters shall directly or authorize other persons toregister. The Minister of Justice shall detail the authorization.
3. Minors and adults who have lost their civil act capacity may requestcivil status registration or issue of civil status extract copies through theirat-law representatives.
1. Commune-level People’s Committees shall make civil statusregistration in the following cases:
a/ Registering civil status events specified at Points a, b, c, d and e,Clause 1, Article 3 of this Law for Vietnamese citizens residing in thecountry;
b/ Registering civil status change and correction for persons under 14full years; addition of civil status information for Vietnamese citizensresiding in the country;
d/ Registering birth for children born in Vietnam with a parent being aVietnamese citizen permanently residing in a border area and the other parentbeing a citizen of the bordering country permanently residing in the area borderingon Vietnam; marriage, recognition of parent or child between Vietnamesecitizens permanently residing in border areas and citizens of borderingcountries permanently residing in areas bordering on Vietnam; and death forforeigners permanently and stably residing in border areas of Vietnam.
2. District-level People’s Committees shall make civil statusregistration in the following cases, except the cases specified at Point d,Clause 1 of this Article:
a/ Registering civil status events specified in Clause 1, Article 3 ofthis Law involving foreign elements;
b/ Registering civil status change and correction for Vietnamesecitizens aged full 14 year or older residing in the country; and ethnicityre-determination;
3. Representative missions shall register civil status matters specifiedin Article 3 of this Law for Vietnamese citizens residing abroad.
4. The Government shall stipulate birth, marriage, parent and childrecognition and death registration procedures prescribed at Point d, Clause 1of this Article.
Article 8. Assurance of the exercise andperformance of the civil status registration right and obligation
1. The State shall adopt comprehensive policies and measures and createconditions for individuals to exercise and perform the civil statusregistration right and obligation.
2. The State shall ensure budget, physical foundations, human resourcesand investment in information technology development for civil statusregistration and management activities.
1. When requesting civil status registration or issue of civil statusextract copies, individuals shall submit dossiers directly to the civil statusregistration agency or send them by post or via the online civil statusregistration system.
2. When carrying out procedures for civil status registration or issueof civil status extract copies from the civil status database, individuals shallproduce papers proving their identity to the civil status registration agency.If sending dossiers by post, they shall send certified copies of these papers.
3. For civil status registration matters for which settlement timelimits have been set, dossier recipients shall write receipts; for incompleteor invalid dossiers, they shall issue written guidance for civil statusregistrants to complete the dossiers. Such written guidance must clearly statetypes of papers to be added.
In case requesters submit dossiers to an improper civil statusregistration agency, dossier recipients shall guide them to submit dossiers tocompetent agencies.
Papers granted, notarized or certified by competent foreign agencies forcivil status registration in Vietnam shall be consularly legalized inaccordance with law, unless they are exempted under a treaty to which Vietnamis a contracting party.
a/ Civil status registration for members of families that have renderedmeritorious services to the revolution; members of poor households; personswith disabilities;
b/ Birth and death registration on time, guardianship and marriage ofVietnamese citizens residing in the country.
2. Individuals who request registration of civil status events otherthan those prescribed in Clause 1 of this Article or issue of civil statusextract copies shall pay a fee.
The Ministry of Finance shall stipulate in detail the competence tocollect, fee rates and the management and use of civil status fees.
a/ Providing untruthful information and documents, forging or usingforged papers or papers of other persons for civil status registration;
b/ Threatening, coercing or hindering the exercise and performance ofthe civil status registration right and obligation;
dd/ Forging, modifying and falsifying contents of civil status papers orinformation in the civil status database;
e/ Giving bribes and promising material or spiritual benefits in orderto obtain civil status registration;
g/ Abusing the civil status registration or shirking the civil statusregistration obligation for self-seeking purpose, enjoying the State’spreferential policy or earning illicit profits in whatever forms;
h/ Persons competent to decide on civil status registration making civilstatus registration for themselves or their relatives under the Law on Marriageand Family;
2. Civil status papers that are granted in cases of civil statusregistration in violation of Points a, d, dd, g and h, Clause 1 of this Articleare all invalid and subject to revocation and cancellation.
3. Individuals who commit any act specified in Clause 1 of this Articleshall, depending on the nature and seriousness of their acts, beadministratively handled or examined for penal liability in accordance withlaw.
Cadres or civil servants who commit the provisions of Clause 1 of thisArticle shall, in addition to being handled as above, be disciplined inaccordance with the law on cadres and civil servants.
Commune-level People’s Committees of the places of residence of fathersor mothers shall make birth registration.
a/ Information of the person whose birth is registered: family name,middle name and first name; gender; birthdate; birthplace; native place;ethnicity; and citizenship;
b/ Information of the parents of the person whose birth is registered:full name, middle name and first name; year of birth; ethnicity; citizenship;and place of residence;
2. The determination of citizenship, ethnicity and family name of aperson whose birth is registered must comply with the law on Vietnamesenationality and civil law.
3. Contents of birth registration specified in Clause 1 of this Articleare basic civil status information of individuals and shall be recorded in thecivil status books and birth certificates and updated in the electronic civilstatus database and national population database. Dossiers and papers ofindividuals related to birth registration information must be consistent withtheir birth registration contents.
The Government shall stipulate the grant of personal identificationnumbers to persons whose birth is registered.
1. Within 60 days after the birth of their child, the father or mothershall register the child’s birth; if the parents are unable to register theirchild’s birth, the grandfather or grandmother or another relative or theindividual or organization that is nurturing the child shall register his/herbirth.
2. Justice and civil status officers shall regularly examine and urgethe birth registration for children in their localities within the prescribedtime limit; in case of necessity, mobile birth registration may be made.
1. Birth registrants shall submit declarations made according to a setform and birth certification papers to the civil status registration agency. Ifhaving no birth certification paper, a document of a witness certifying thebirth shall be submitted; if there is no witness, there must be a writtenpledge of the birth; for birth registration for abandoned children, there mustbe a written record certifying the child’s abandonment made by a competentagency; for birth registration for children born by surrogate mothers, theremust be a document proving the surrogacy as prescribed by law.
Xem thêm: Sản Xuất Là Gì – Tổ Chức ý Nghĩa Và Mục đích
2. Immediately after receiving full papers specified in Clause 1 of thisArticle, if seeing that the birth declaration is complete and proper, justiceand civil status officers shall record birth registration contents under Clause1, Article 14 of this Law in the civil status books and update them in theelectronic civil status database and the national population database forgetting personal identification numbers.
Justice and civil status officers and birth registrants shall togethersign in the civil status books. Chairpersons of commune-level People’sCommittees shall grant birth certificates to birth registrants.
3. The Government shall stipulate in detail the birth registration forabandoned children and children whose parents have not yet been identified dueto surrogacy; and the determination of native places for abandoned children andchildren with unidentified parents.

Chuyên mục: Hỏi Đáp